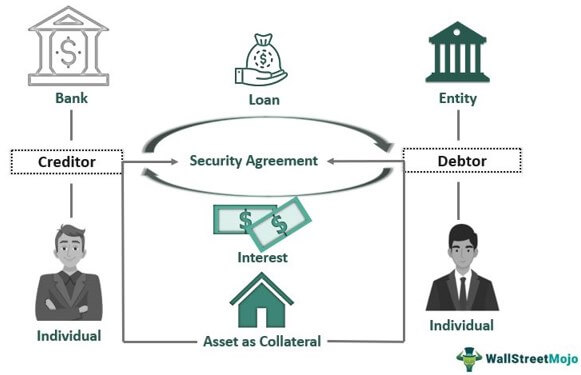
Creditors play a crucial role in the financial system, yet their function is often misunderstood. In one sentence a creditor is an individual or institution that extends credit to another party, allowing them to borrow money that is to be repaid at a future date. This concise definition captures the essence of what a creditor is, but there are some important details to expand upon.
Breaking Down the Definition
The single sentence definition contains several key components that require further explanation
Individual or Institution
They can be a person or a business like a bank, credit union, or other financial institution. Creditors offer long-term loans like credit cards, lines of credit, and more, as well as short-term loans for things like cars and homes.
Extends Credit
The act of extending credit means allowing another party, known as the debtor, to use the creditor’s money or assets with the expectation they will be repaid. Common types of credit extensions include loans, bonds, notes, and accounts receivable.
Another Party
The person who gets credit is called the debtor or borrower. This is the person or business that agrees to borrow money and pay it back.
Borrow Money
The creditor lends money or assets that enable the debtor to make purchases or investments they otherwise could not afford upfront. This borrowed money must eventually be repaid to the creditor per the lending agreement.
Repaid at a Future Date
There is a timeline for repayment set by the creditor. Loans for a short time may be paid back in a few weeks or months, but mortgages and other long-term loans can take decades to pay off. When you borrow money, you usually have to pay interest on it.
When put together, these key phrases say everything you need to know about a creditor in one sentence. However, why is this definition important? What are some examples of creditors at work?
The Importance of Understanding Creditors
Defining creditors clearly is important for several reasons:
-
Financial literacy – Knowing the correct terminology improves financial literacy and understanding of basic lending concepts. This knowledge helps consumers make wise borrowing decisions.
-
Business finance – Entrepreneurs need to identify and manage relationships with their creditors including lenders, suppliers, bondholders, and shareholders.
-
Accounting and bookkeeping – Creditors appear on a company’s balance sheet as liabilities. The accounts payable department handles accounting and payment of creditors.
-
Investing – Investors analyze a company’s debt levels and ability to meet creditor obligations before providing financing through bonds or stock purchases.
-
Consumer protection – Consumers must understand creditors’ rights and responsibilities when they take on a loan or debt. Predatory lending practices by unscrupulous creditors should raise red flags.
Having a concise definition helps reinforce these important contexts surrounding creditors in everyday finance and business.
Examples of Creditors
Some common examples of creditors include:
-
Banks – Banks and credit unions that provide loans and lines of credit to individuals and businesses are creditors. They allow depositors to borrow their capital.
-
Mortgage Companies – Mortgage lenders provide financing for home buyers. The borrowed money must be repaid over 15-30 years. Interest charges apply.
-
Credit Card Companies – Issuers of consumer and business credit cards such as Visa, MasterCard, and American Express are creditors providing revolving credit lines.
-
Suppliers – Companies that provide business inventory on credit are trade creditors awaiting payment in the future for goods received today.
-
Bond Investors – Organizations that purchase corporate or municipal bonds become creditors that must be repaid principal plus interest.
-
Shareholders – Equity investors provide capital in exchange for partial ownership and expect dividend payments. They are creditors from an accounting perspective.
Government Agencies – Federal and state entities lend money to individuals, businesses, and other agencies through loans, grants, and financing programs.
These examples demonstrate the wide range of institutions and relationships that fit the one sentence creditors definition. Anytime someone lends money that must be repaid in the future, they are considered a creditor.
In Summary
Defining creditors succinctly helps clarify their vital role in finance and lending. The concise one sentence explanation is:
A creditor is an individual or institution that extends credit to another party, allowing them to borrow money that is to be repaid at a future date.
This simple definition may not capture all the nuances and complexities of creditors. But it provides a solid foundation for understanding these important participants in every economy. Taking time to learn basic terminology empowers consumers, business owners, and professionals to make smart financial decisions and build win-win relationships between creditors and debtors.
Influence of the Accounts Payable Target on Business Practice
The accounts payable target influences various aspects of Corporate Management and planning:
- Cash flow management: longer accounts payable terms improve short-term cash flow by allowing the company to utilize available cash longer before having to settle accounts payable.
- Accounting: Accounts payable targets affect the presentation of current liabilities on the balance sheet and can therefore represent the financial health of the company to the outside world.
- Strategic decisions: Companies also use accounts payable targets strategically to increase their bargaining power with suppliers and negotiate better terms.
A well-managed accounts payable target helps to secure a companys financial stability, optimize its liquidity and maintain stable business relationships with suppliers.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Creditor | Supplier or service provider who supplies goods or services to a company on a credit basis. |
| Liability | Financial obligation of a company to a creditor that must be settled at a later date. |
| Receivable | The creditors claim to payment for goods delivered or services rendered. |
| Payment term | The period within which the liability to the creditor must be settled. |
| Revolving Credit | Short-term credit line granted by a creditor to a company, often to bridge liquidity bottlenecks. |
| Supplier credit | Credit granted by a supplier to a customer in the form of a payment term. |
| Accounts payable | Department or function within a company that deals with the administration and posting of liabilities to creditors. |
| Invoice receipt ledger | List of all incoming invoices from creditors, used for control and tracking purposes. |
| Cashback | Price reduction granted by a creditor if an invoice is paid within a certain period of time. |
| Credit note | Document that represents a correction or refund of amounts already invoiced. |
| Credit rating | Assessment of the creditworthiness of a company by a creditor. |
| Credit period | The average amount of time it takes a company to settle its debts to creditors. |
| Due date | The date on which a liability must be settled. |
| Reminder | Reminder letter from the creditor to the debtor that a payment is overdue. |
| Delayed payment | A situation in which a company fails to settle its liabilities on time. |
| Liquidity | The ability of a company to pay its current liabilities on time. |
| Balance sheet | Financial report that shows the assets, liabilities and equity of a company at a specific point in time. |
| General ledger | Central accounting ledger in which all business transactions of a company are recorded chronologically. |
| Creditor number | Unique identification number assigned to a creditor in a companys accounting system. |
| Purchasing department | Department within a company that is responsible for purchasing goods and services and often negotiates with creditors. |
This table provides a compact overview of the most important terms relating to creditors and their definitions.
Meaning of Creditor: Where does the word come from?
The word “creditor” comes from Latin and is derived from the verb “credere”, which means “to believe” or “to trust”. A creditor is someone who places trust in another by supplying goods or services on a credit basis, i.e. without immediate payment. The term thus reflects the trust that the supplier or service provider places in the buyer that the latter will settle his debt at a later date. In business and finance, the creditor is therefore a central figure who ensures the financing and smooth flow of goods and services between companies.
Creditors Reconciliation | Creditors Control & Creditors Ledger | Explained with Example
FAQ
What is creditor in one sentence?
The company said it would pay in full all its creditors. The company said it would pay in full all its creditors. A provisional liquidator can either restructure or liquidate assets and distribute proceeds to creditors. A creditor is an organization or person who people owe money to.
What is the meaning of creditors?
A person who is owed money and has the right to demand that the money be paid to them A creditor may have a claim of payment against a debtor that is either liquidated or unliquidated.
What is debtors answer in one sentence?
A debtor is an individual, business, or entity that owes money to another party, known as the creditor.
Who is a creditor in your own words?
A creditor is a natural or legal person who supplies goods or services to a company on a credit basis. This means that the company doesn’t pay right away for the goods or services it receives; instead, it owes the creditor money that it will pay back later.
